Global Virtual Reality In Healthcare Market Size, Share & Trends Analysis Report, Forecast Period, 2024-2030
Report ID: MS-859 | Healthcare and Pharma | Last updated: May, 2025 | Formats*:
The virtual reality in healthcare market can be defined as the industry comprising the creation, distribution, and implementation of virtual reality technologies and software applications especially tailored for the healthcare sector. VR here refers to the simulation of immersive, interactive, and simulated environments in which users immerse themselves with headsets and other sensory gadgets. These virtual experiences are utilised for a broad range of healthcare purposes, from medical education and surgical planning to pain management, rehabilitation, mental health treatment, and patient education. The market consists of hardware companies, software companies, content providers, and the healthcare providers and institutions that use these VR solutions.
Virtual Reality In Healthcare Report Highlights
| Report Metrics | Details |
|---|---|
| Forecast period | 2019-2030 |
| Base Year Of Estimation | 2024 |
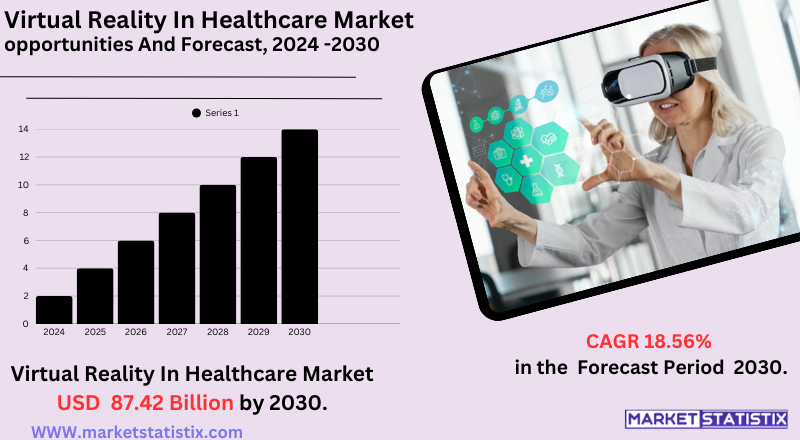
| Growth Rate | CAGR of 18.56% |
| Forecast Value (2030) | USD 87.42 Billion |
| By Product Type | Hardware, Software, Services |
| Key Market Players |
|
| By Region |
|
Virtual Reality In Healthcare Market Trends
Some major trends are driving the VR in Healthcare market. First, growing use of VR for medical training and education is a major factor, with VR simulations providing realistic, hands-on experiences for surgeons, doctors, and medical students. Second, VR is finding increasing use in pain management through immersive distractions that can help patients decrease their use of medication. Thirdly, its use in mental illness, especially for PTSD, anxiety disorder, and phobia treatments with virtual exposure therapy, is gaining ground. Besides, it combining with telemedicine is enhancing distance patient care and accessibility.
Virtual Reality In Healthcare Market Leading Players
The key players profiled in the report are Qualcomm Technologies Inc. (United States), Siemens (Germany), General Electric (United States, CAE Healthcare (United States), Brainlab AG (Germany), Samsung (South Korea), Mimic Technologies Inc (United States), PSICO SMART APPS, S.L. (Spain, Koninklijke Philips N.V (Netherlands), Medical Realities Ltd (U.K.), Virtual Realities LLC (U.K.), ImmersiveTouch, Inc (United States), Virtalis (U.K.), Firsthand (United States, Vuzix (United States)Growth Accelerators
The Virtual Reality (VR) in Healthcare Market is driven by a number of important factors. First, the growing need for quality healthcare requires creative solutions to medical training to enable professionals to practise complex procedures in a risk-free simulated environment, which increases their competence and minimises errors in actual circumstances. Secondly, the necessity of curbing spiralling healthcare expenditure propels the use of VR for purposes such as remote monitoring of patients, virtual consultations, and effective training modules, saving costs related to conventional approaches.
In addition, the increasing level of connected devices in the healthcare system provides fertile ground for adopting VR, which facilitates effortless visualisation of data and real-time collaboration among medical staff. Advances in VR hardware and software technology, which make them increasingly affordable and easy to use, combined with increasing investments in telemedicine and digital health, also fuel market expansion. The success of VR across various applications, including pain care, rehabilitation, mental therapy, and education for patients, further fuels its growing adoption and use in the healthcare sector.
Virtual Reality In Healthcare Market Segmentation analysis
The Global Virtual Reality In Healthcare is segmented by Type, Application, and Region. By Type, the market is divided into Distributed Hardware, Software, Services . The Application segment categorizes the market based on its usage such as Hospitals, Clinics, Diagnostic Centers, Rehabilitation Centers, Surgical Centers, Ambulatory Surgical Centers, Mental Health Institutions, Others. Geographically, the market is assessed across key Regions like North America (United States, Canada, Mexico), South America (Brazil, Argentina, Chile, Rest of South America), Europe (Germany, France, Italy, United Kingdom, Benelux, Nordics, Rest of Europe), Asia Pacific (China, Japan, India, South Korea, Australia, Southeast Asia, Rest of Asia-Pacific), MEA (Middle East, Africa) and others, each presenting distinct growth opportunities and challenges influenced by the regions.Competitive Landscape
The Virtual Reality (VR) in Healthcare Market's competitive scenario is becoming ever more dynamic with the presence of a mix of incumbent technology titans, specialist VR hardware and software vendors, and healthcare-focused enterprises. Incumbents are continually innovating on the dimensions of headset technology, software design for particular medical purposes (such as surgical simulation, pain therapy, and mental illness therapy), and the blending of VR with other emerging technologies such as AI and augmented reality (AR).
Competition is growing as the potential of VR to revolutionise healthcare delivery and training becomes clearer. Major differentiators between firms are the degree of immersion and realism delivered by their VR platforms, the ease of use and integration capabilities of their software, the scope of healthcare applications they support, and their capacity to comply with strict regulatory demands and security levels. In addition, cost-effectiveness and the capacity to show clear clinical and economic value are essential to gaining momentum in this emerging market. As more investment and research are being put into this area, the competitive environment is likely to become increasingly crowded and innovative in the years ahead, ultimately serving healthcare providers and patients with more sophisticated and accessible VR solutions.
Challenges In Virtual Reality In Healthcare Market
The healthcare virtual reality (VR) market is beset by some key challenges that slow down integration and adoption. They include prohibitive acquisition and maintenance costs, hesitation regarding the cost-benefit ratio, and insufficient reimbursement of VR-based therapy, which leaves most healthcare providers in a situation where they are hard-pressed to justify spending on it. Moreover, technical constraints like immature hardware and software, device bulkiness issues, poor-quality graphics, and risks of cybersickness also hinder adoption. Several clinicians also report a lack of proper facilities, poor technical support, and inadequate funding as continuing barriers.
Organisational and professional barriers are limited knowledge and training among health professionals, doubt regarding the clinical effectiveness of VR, and practical implementation problems within health facilities. Bureaucratic barriers, incompatibility with current healthcare IT systems, and sluggish procurement also impede the rate of adoption. Additionally, cultural and geographic variations, coupled with resistance from some stakeholders, complicate market penetration. Overcoming these hurdles requires the industry to emphasise elevating technology maturity, increasing training programmes, and encouraging collaboration among developers and healthcare providers to produce solutions that meet actual clinical requirements.
Risks & Prospects in Virtual Reality In Healthcare Market
Key areas of growth are in personalised rehabilitation protocols, multilingual and culturally adapted VR platforms, and creating advanced therapy and training platforms. Hardware, particularly VR headsets, is the biggest market because it plays a central role in medical simulation and surgery planning, whereas the most rapidly expanding area is rehabilitation and therapy because VR can provide compelling and effective treatments for physical and mental disorders.
Geographically, North America dominates the market, aided by a strong healthcare ecosystem, early health technology adoption, and high investments in innovation. The United States stands to gain the most from high concentrations of leading players and government support for virtual healthcare projects. The Asia-Pacific is growing at the fastest pace, driven by high rates of technology adoption, growing healthcare investments, and favourable government policies. China, India, and Japan are already aggressively adopting VR in medical school, patient treatment, and therapies for mental health, and so the area is a hotbed for future growth opportunities.
Key Target Audience
The healthcare market for virtual reality (VR) addresses a broad base of people, with hospitals, clinics, and surgery centers being major users. These facilities leverage VR for uses in surgical simulation, pain control, patient care, and rehab. The use of VR in these environments improves patient outcomes and operational effectiveness.
,,,, ,,
Moreover, medical schools and universities are also major stakeholders, utilising VR to offer engaging learning experiences to students. The technology enables realistic simulations of medical procedures for enhanced skill acquisition and retention. Pharmaceutical firms and research institutions also use VR to develop drugs and conduct clinical trials, using virtual environments to replicate molecular structures and patient interactions. In addition, technology vendors have a significant role by creating and providing VR hardware and software specifically for healthcare use, responding to the increasing need for innovative solutions within the sector.
,,
Merger and acquisition
The healthcare virtual reality (VR) market has seen a lot of merger and acquisition (M&A) activity over the last few years, indicating a shift towards consolidation and innovation. In May 2024, Akili, which is a digital therapeutics firm, announced that it had entered into a merger with Virtual Therapeutics to merge Akili's mobile digital therapeutics with Virtual Therapeutics' VR-based mental health treatments. This strategic step is likely to form a diversified digital health firm better positioned to meet diverse mental health requirements. Likewise, in February 2024, the National Board of Medical Examiners (NBME) purchased MedVR Education, a VR-based medical training company. This purchase is intended to bolster NBME's strength in creating innovative tools and assessments for medical education.
These M&A efforts highlight the increasing significance of VR technologies within the healthcare sector, especially in applications such as mental health care and medical training. The introduction of VR to healthcare services is not only improving patient outcomes but also transforming how medical professionals are educated. With the industry continuing to consolidate and form strategic alliances, additional consolidation and strategic alliances are expected to drive innovation and increase the penetration of VR applications within the healthcare industry.
>
Analyst Comment
The healthcare virtual reality (VR) market is growing rapidly and exponentially, with the size of the global market expected to hit around USD 6.02 billion in 2025 and expected to reach around USD 29.13 billion by 2029. The growth is fuelled by growing use of VR for medical training, management of patient care, pain management, remote consultations, and immersive therapy for neurological and psychological disorders. VR technologies are revolutionising healthcare delivery through simulation-based medical professional training, patient engagement improvement, and enabling minimally invasive procedures and real-time surgical guidance.
- 1.1 Report description
- 1.2 Key market segments
- 1.3 Key benefits to the stakeholders
2: Executive Summary
- 2.1 Virtual Reality In Healthcare- Snapshot
- 2.2 Virtual Reality In Healthcare- Segment Snapshot
- 2.3 Virtual Reality In Healthcare- Competitive Landscape Snapshot
3: Market Overview
- 3.1 Market definition and scope
- 3.2 Key findings
- 3.2.1 Top impacting factors
- 3.2.2 Top investment pockets
- 3.3 Porter’s five forces analysis
- 3.3.1 Low bargaining power of suppliers
- 3.3.2 Low threat of new entrants
- 3.3.3 Low threat of substitutes
- 3.3.4 Low intensity of rivalry
- 3.3.5 Low bargaining power of buyers
- 3.4 Market dynamics
- 3.4.1 Drivers
- 3.4.2 Restraints
- 3.4.3 Opportunities
4: Virtual Reality In Healthcare Market by Type
- 4.1 Overview
- 4.1.1 Market size and forecast
- 4.2 Hardware
- 4.2.1 Key market trends, factors driving growth, and opportunities
- 4.2.2 Market size and forecast, by region
- 4.2.3 Market share analysis by country
- 4.3 Software
- 4.3.1 Key market trends, factors driving growth, and opportunities
- 4.3.2 Market size and forecast, by region
- 4.3.3 Market share analysis by country
- 4.4 Services
- 4.4.1 Key market trends, factors driving growth, and opportunities
- 4.4.2 Market size and forecast, by region
- 4.4.3 Market share analysis by country
5: Virtual Reality In Healthcare Market by Application / by End Use
- 5.1 Overview
- 5.1.1 Market size and forecast
- 5.2 Hospitals
- 5.2.1 Key market trends, factors driving growth, and opportunities
- 5.2.2 Market size and forecast, by region
- 5.2.3 Market share analysis by country
- 5.3 Clinics
- 5.3.1 Key market trends, factors driving growth, and opportunities
- 5.3.2 Market size and forecast, by region
- 5.3.3 Market share analysis by country
- 5.4 Surgical Centers
- 5.4.1 Key market trends, factors driving growth, and opportunities
- 5.4.2 Market size and forecast, by region
- 5.4.3 Market share analysis by country
- 5.5 Ambulatory Surgical Centers
- 5.5.1 Key market trends, factors driving growth, and opportunities
- 5.5.2 Market size and forecast, by region
- 5.5.3 Market share analysis by country
- 5.6 Diagnostic Centers
- 5.6.1 Key market trends, factors driving growth, and opportunities
- 5.6.2 Market size and forecast, by region
- 5.6.3 Market share analysis by country
- 5.7 Rehabilitation Centers
- 5.7.1 Key market trends, factors driving growth, and opportunities
- 5.7.2 Market size and forecast, by region
- 5.7.3 Market share analysis by country
- 5.8 Mental Health Institutions
- 5.8.1 Key market trends, factors driving growth, and opportunities
- 5.8.2 Market size and forecast, by region
- 5.8.3 Market share analysis by country
- 5.9 Others
- 5.9.1 Key market trends, factors driving growth, and opportunities
- 5.9.2 Market size and forecast, by region
- 5.9.3 Market share analysis by country
6: Virtual Reality In Healthcare Market by Region
- 6.1 Overview
- 6.1.1 Market size and forecast By Region
- 6.2 North America
- 6.2.1 Key trends and opportunities
- 6.2.2 Market size and forecast, by Type
- 6.2.3 Market size and forecast, by Application
- 6.2.4 Market size and forecast, by country
- 6.2.4.1 United States
- 6.2.4.1.1 Key market trends, factors driving growth, and opportunities
- 6.2.4.1.2 Market size and forecast, by Type
- 6.2.4.1.3 Market size and forecast, by Application
- 6.2.4.2 Canada
- 6.2.4.2.1 Key market trends, factors driving growth, and opportunities
- 6.2.4.2.2 Market size and forecast, by Type
- 6.2.4.2.3 Market size and forecast, by Application
- 6.2.4.3 Mexico
- 6.2.4.3.1 Key market trends, factors driving growth, and opportunities
- 6.2.4.3.2 Market size and forecast, by Type
- 6.2.4.3.3 Market size and forecast, by Application
- 6.2.4.1 United States
- 6.3 South America
- 6.3.1 Key trends and opportunities
- 6.3.2 Market size and forecast, by Type
- 6.3.3 Market size and forecast, by Application
- 6.3.4 Market size and forecast, by country
- 6.3.4.1 Brazil
- 6.3.4.1.1 Key market trends, factors driving growth, and opportunities
- 6.3.4.1.2 Market size and forecast, by Type
- 6.3.4.1.3 Market size and forecast, by Application
- 6.3.4.2 Argentina
- 6.3.4.2.1 Key market trends, factors driving growth, and opportunities
- 6.3.4.2.2 Market size and forecast, by Type
- 6.3.4.2.3 Market size and forecast, by Application
- 6.3.4.3 Chile
- 6.3.4.3.1 Key market trends, factors driving growth, and opportunities
- 6.3.4.3.2 Market size and forecast, by Type
- 6.3.4.3.3 Market size and forecast, by Application
- 6.3.4.4 Rest of South America
- 6.3.4.4.1 Key market trends, factors driving growth, and opportunities
- 6.3.4.4.2 Market size and forecast, by Type
- 6.3.4.4.3 Market size and forecast, by Application
- 6.3.4.1 Brazil
- 6.4 Europe
- 6.4.1 Key trends and opportunities
- 6.4.2 Market size and forecast, by Type
- 6.4.3 Market size and forecast, by Application
- 6.4.4 Market size and forecast, by country
- 6.4.4.1 Germany
- 6.4.4.1.1 Key market trends, factors driving growth, and opportunities
- 6.4.4.1.2 Market size and forecast, by Type
- 6.4.4.1.3 Market size and forecast, by Application
- 6.4.4.2 France
- 6.4.4.2.1 Key market trends, factors driving growth, and opportunities
- 6.4.4.2.2 Market size and forecast, by Type
- 6.4.4.2.3 Market size and forecast, by Application
- 6.4.4.3 Italy
- 6.4.4.3.1 Key market trends, factors driving growth, and opportunities
- 6.4.4.3.2 Market size and forecast, by Type
- 6.4.4.3.3 Market size and forecast, by Application
- 6.4.4.4 United Kingdom
- 6.4.4.4.1 Key market trends, factors driving growth, and opportunities
- 6.4.4.4.2 Market size and forecast, by Type
- 6.4.4.4.3 Market size and forecast, by Application
- 6.4.4.5 Benelux
- 6.4.4.5.1 Key market trends, factors driving growth, and opportunities
- 6.4.4.5.2 Market size and forecast, by Type
- 6.4.4.5.3 Market size and forecast, by Application
- 6.4.4.6 Nordics
- 6.4.4.6.1 Key market trends, factors driving growth, and opportunities
- 6.4.4.6.2 Market size and forecast, by Type
- 6.4.4.6.3 Market size and forecast, by Application
- 6.4.4.7 Rest of Europe
- 6.4.4.7.1 Key market trends, factors driving growth, and opportunities
- 6.4.4.7.2 Market size and forecast, by Type
- 6.4.4.7.3 Market size and forecast, by Application
- 6.4.4.1 Germany
- 6.5 Asia Pacific
- 6.5.1 Key trends and opportunities
- 6.5.2 Market size and forecast, by Type
- 6.5.3 Market size and forecast, by Application
- 6.5.4 Market size and forecast, by country
- 6.5.4.1 China
- 6.5.4.1.1 Key market trends, factors driving growth, and opportunities
- 6.5.4.1.2 Market size and forecast, by Type
- 6.5.4.1.3 Market size and forecast, by Application
- 6.5.4.2 Japan
- 6.5.4.2.1 Key market trends, factors driving growth, and opportunities
- 6.5.4.2.2 Market size and forecast, by Type
- 6.5.4.2.3 Market size and forecast, by Application
- 6.5.4.3 India
- 6.5.4.3.1 Key market trends, factors driving growth, and opportunities
- 6.5.4.3.2 Market size and forecast, by Type
- 6.5.4.3.3 Market size and forecast, by Application
- 6.5.4.4 South Korea
- 6.5.4.4.1 Key market trends, factors driving growth, and opportunities
- 6.5.4.4.2 Market size and forecast, by Type
- 6.5.4.4.3 Market size and forecast, by Application
- 6.5.4.5 Australia
- 6.5.4.5.1 Key market trends, factors driving growth, and opportunities
- 6.5.4.5.2 Market size and forecast, by Type
- 6.5.4.5.3 Market size and forecast, by Application
- 6.5.4.6 Southeast Asia
- 6.5.4.6.1 Key market trends, factors driving growth, and opportunities
- 6.5.4.6.2 Market size and forecast, by Type
- 6.5.4.6.3 Market size and forecast, by Application
- 6.5.4.7 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 6.5.4.7.1 Key market trends, factors driving growth, and opportunities
- 6.5.4.7.2 Market size and forecast, by Type
- 6.5.4.7.3 Market size and forecast, by Application
- 6.5.4.1 China
- 6.6 MEA
- 6.6.1 Key trends and opportunities
- 6.6.2 Market size and forecast, by Type
- 6.6.3 Market size and forecast, by Application
- 6.6.4 Market size and forecast, by country
- 6.6.4.1 Middle East
- 6.6.4.1.1 Key market trends, factors driving growth, and opportunities
- 6.6.4.1.2 Market size and forecast, by Type
- 6.6.4.1.3 Market size and forecast, by Application
- 6.6.4.2 Africa
- 6.6.4.2.1 Key market trends, factors driving growth, and opportunities
- 6.6.4.2.2 Market size and forecast, by Type
- 6.6.4.2.3 Market size and forecast, by Application
- 6.6.4.1 Middle East
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Key Winning Strategies
- 7.3 Top 10 Players: Product Mapping
- 7.4 Competitive Analysis Dashboard
- 7.5 Market Competition Heatmap
- 7.6 Leading Player Positions, 2022
8: Company Profiles
- 8.1 Brainlab AG (Germany)
- 8.1.1 Company Overview
- 8.1.2 Key Executives
- 8.1.3 Company snapshot
- 8.1.4 Active Business Divisions
- 8.1.5 Product portfolio
- 8.1.6 Business performance
- 8.1.7 Major Strategic Initiatives and Developments
- 8.2 CAE Healthcare (United States)
- 8.2.1 Company Overview
- 8.2.2 Key Executives
- 8.2.3 Company snapshot
- 8.2.4 Active Business Divisions
- 8.2.5 Product portfolio
- 8.2.6 Business performance
- 8.2.7 Major Strategic Initiatives and Developments
- 8.3 Firsthand (United States
- 8.3.1 Company Overview
- 8.3.2 Key Executives
- 8.3.3 Company snapshot
- 8.3.4 Active Business Divisions
- 8.3.5 Product portfolio
- 8.3.6 Business performance
- 8.3.7 Major Strategic Initiatives and Developments
- 8.4 General Electric (United States
- 8.4.1 Company Overview
- 8.4.2 Key Executives
- 8.4.3 Company snapshot
- 8.4.4 Active Business Divisions
- 8.4.5 Product portfolio
- 8.4.6 Business performance
- 8.4.7 Major Strategic Initiatives and Developments
- 8.5 ImmersiveTouch
- 8.5.1 Company Overview
- 8.5.2 Key Executives
- 8.5.3 Company snapshot
- 8.5.4 Active Business Divisions
- 8.5.5 Product portfolio
- 8.5.6 Business performance
- 8.5.7 Major Strategic Initiatives and Developments
- 8.6 Inc (United States)
- 8.6.1 Company Overview
- 8.6.2 Key Executives
- 8.6.3 Company snapshot
- 8.6.4 Active Business Divisions
- 8.6.5 Product portfolio
- 8.6.6 Business performance
- 8.6.7 Major Strategic Initiatives and Developments
- 8.7 Koninklijke Philips N.V (Netherlands)
- 8.7.1 Company Overview
- 8.7.2 Key Executives
- 8.7.3 Company snapshot
- 8.7.4 Active Business Divisions
- 8.7.5 Product portfolio
- 8.7.6 Business performance
- 8.7.7 Major Strategic Initiatives and Developments
- 8.8 Medical Realities Ltd (U.K.)
- 8.8.1 Company Overview
- 8.8.2 Key Executives
- 8.8.3 Company snapshot
- 8.8.4 Active Business Divisions
- 8.8.5 Product portfolio
- 8.8.6 Business performance
- 8.8.7 Major Strategic Initiatives and Developments
- 8.9 Mimic Technologies Inc (United States)
- 8.9.1 Company Overview
- 8.9.2 Key Executives
- 8.9.3 Company snapshot
- 8.9.4 Active Business Divisions
- 8.9.5 Product portfolio
- 8.9.6 Business performance
- 8.9.7 Major Strategic Initiatives and Developments
- 8.10 PSICO SMART APPS
- 8.10.1 Company Overview
- 8.10.2 Key Executives
- 8.10.3 Company snapshot
- 8.10.4 Active Business Divisions
- 8.10.5 Product portfolio
- 8.10.6 Business performance
- 8.10.7 Major Strategic Initiatives and Developments
- 8.11 S.L. (Spain
- 8.11.1 Company Overview
- 8.11.2 Key Executives
- 8.11.3 Company snapshot
- 8.11.4 Active Business Divisions
- 8.11.5 Product portfolio
- 8.11.6 Business performance
- 8.11.7 Major Strategic Initiatives and Developments
- 8.12 Qualcomm Technologies Inc. (United States)
- 8.12.1 Company Overview
- 8.12.2 Key Executives
- 8.12.3 Company snapshot
- 8.12.4 Active Business Divisions
- 8.12.5 Product portfolio
- 8.12.6 Business performance
- 8.12.7 Major Strategic Initiatives and Developments
- 8.13 Samsung (South Korea)
- 8.13.1 Company Overview
- 8.13.2 Key Executives
- 8.13.3 Company snapshot
- 8.13.4 Active Business Divisions
- 8.13.5 Product portfolio
- 8.13.6 Business performance
- 8.13.7 Major Strategic Initiatives and Developments
- 8.14 Siemens (Germany)
- 8.14.1 Company Overview
- 8.14.2 Key Executives
- 8.14.3 Company snapshot
- 8.14.4 Active Business Divisions
- 8.14.5 Product portfolio
- 8.14.6 Business performance
- 8.14.7 Major Strategic Initiatives and Developments
- 8.15 Virtual Realities LLC (U.K.)
- 8.15.1 Company Overview
- 8.15.2 Key Executives
- 8.15.3 Company snapshot
- 8.15.4 Active Business Divisions
- 8.15.5 Product portfolio
- 8.15.6 Business performance
- 8.15.7 Major Strategic Initiatives and Developments
- 8.16 Virtalis (U.K.)
- 8.16.1 Company Overview
- 8.16.2 Key Executives
- 8.16.3 Company snapshot
- 8.16.4 Active Business Divisions
- 8.16.5 Product portfolio
- 8.16.6 Business performance
- 8.16.7 Major Strategic Initiatives and Developments
- 8.17 Vuzix (United States)
- 8.17.1 Company Overview
- 8.17.2 Key Executives
- 8.17.3 Company snapshot
- 8.17.4 Active Business Divisions
- 8.17.5 Product portfolio
- 8.17.6 Business performance
- 8.17.7 Major Strategic Initiatives and Developments
9: Analyst Perspective and Conclusion
- 9.1 Concluding Recommendations and Analysis
- 9.2 Strategies for Market Potential
Scope of Report
| Aspects | Details |
|---|---|
By Type |
|
By Application |
|
Report Licenses
Our Team

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ):
What is the projected market size of Virtual Reality In Healthcare in 2030?
+
-
Which application type is expected to remain the largest segment in the Global Virtual Reality In Healthcare market?
+
-
How big is the Global Virtual Reality In Healthcare market?
+
-
How do regulatory policies impact the Virtual Reality In Healthcare Market?
+
-
What major players in Virtual Reality In Healthcare Market?
+
-
What applications are categorized in the Virtual Reality In Healthcare market study?
+
-
Which product types are examined in the Virtual Reality In Healthcare Market Study?
+
-
Which regions are expected to show the fastest growth in the Virtual Reality In Healthcare market?
+
-
Which application holds the second-highest market share in the Virtual Reality In Healthcare market?
+
-
What are the major growth drivers in the Virtual Reality In Healthcare market?
+
-
The Virtual Reality (VR) in Healthcare Market is driven by a number of important factors. First, the growing need for quality healthcare requires creative solutions to medical training to enable professionals to practise complex procedures in a risk-free simulated environment, which increases their competence and minimises errors in actual circumstances. Secondly, the necessity of curbing spiralling healthcare expenditure propels the use of VR for purposes such as remote monitoring of patients, virtual consultations, and effective training modules, saving costs related to conventional approaches.
In addition, the increasing level of connected devices in the healthcare system provides fertile ground for adopting VR, which facilitates effortless visualisation of data and real-time collaboration among medical staff. Advances in VR hardware and software technology, which make them increasingly affordable and easy to use, combined with increasing investments in telemedicine and digital health, also fuel market expansion. The success of VR across various applications, including pain care, rehabilitation, mental therapy, and education for patients, further fuels its growing adoption and use in the healthcare sector.

